
Diabetes
Advertisement
Topics included the use of technology to manage diabetes and the psychologic impact of hypoglycemia during fasting.
English-only speakers were more likely to adhere to annual HBA1C screening guidelines.
Transgender patients with diabetes have increased risk of complications but lower use of antidiabetic medications.
A community-based program was found to improve QOL for patients with varying levels of social vulnerability.
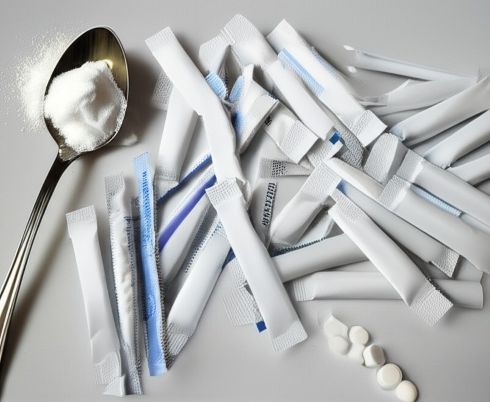
The findings suggest that approximately one-fifth of Americans who consume diet drinks may benefit from this substitution.
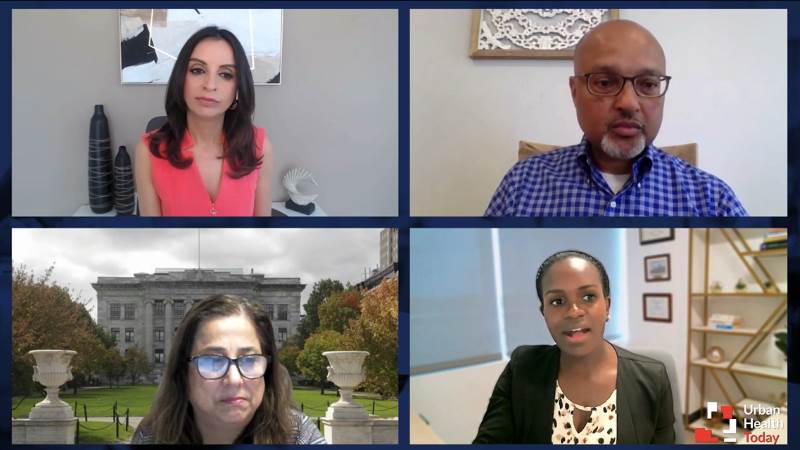
Panelists call on fellow healthcare practitioners to create progress in reducing disparities in T2D over the next decade.
Experts discuss strategies for system-level changes to improve multidisciplinary collaboration and improve diabetes outcomes.
Margaret Zupa, MD, and colleagues found that increased telehealth use since COVID-19 has not improved access to specialists.
The panel explores the impact of health disparities on heart and kidney complications of T2D.
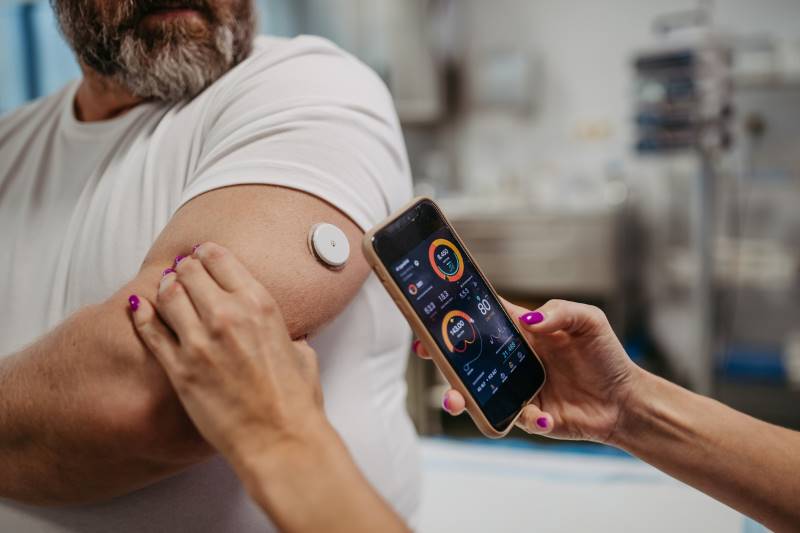
Black and Hispanic patients were less likely to initiate use of continuous glucose monitoring devices.
The study found that participants consuming the most diet beverages had more than double the diabetes risk.
Social determinants of health can create barriers to referrals, diagnostics, and treatment for type 2 diabetes.
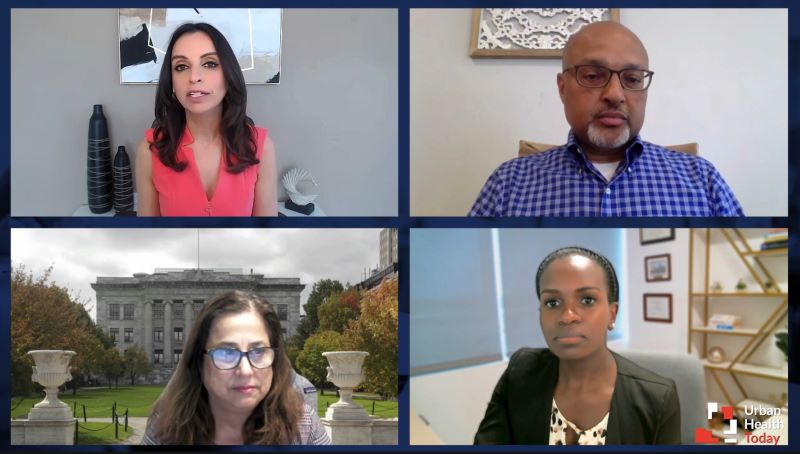
A multidisciplinary panel shares how social determinants of health impact patient care in their respective practices.
Researchers urge early weight management as a potential strategy to reduce long-term metabolic effects of air pollution.
An AI-based digital tool provided effective insulin dosage titration recommendations for inpatients with type 2 diabetes.
Age influences myocardial flow reserve differently in men and women, with women showing a slower decline.
The study demonstrates a strong association between metabolic syndrome and young-onset dementia.
Addressing housing stability alone may not be enough to improve diabetes outcomes.
Researchers evaluated feasibility, acceptability, and preliminary efficacy of a patient portal designed for self-management.
The researchers also found that the risk of sudden cardiac death was significantly elevated in younger individuals.
















 © 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.
© 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.