Pediatric
Advertisement
Avocados contain vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals that support immune and metabolic health.
Public health efforts are needed to raise awareness of early allergen introduction guidelines.
Families reported the direct cash support program offered them the “ability to spend more time at their child’s ...
Food insecurity affects 25% of children with cancer at diagnosis.
Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients were less likely to be started on subcutaneous allergen immunotherapy.
Black children being treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia were twice as likely to have grade ≥3 hyperglycemia.
Outcomes for patients with intermediate-risk disease biology may be most influenced by social determinants of health.
Up to one-third of patients who reported food, housing, or utility insecurity also had private insurance.
More than 60% of patients reported discontinuing treatment due to social factors.
Children who were overweight or obese had a greater risk of a new diabetes diagnosis within 6 months of COVID-19 infection.
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody approved to treat atopic dermatitis in adolescents and children.
The risk of seizure was higher in children aged 6 to 24 months.
The panelists discuss how health care providers can get involved in creating allergy action plans and kits.
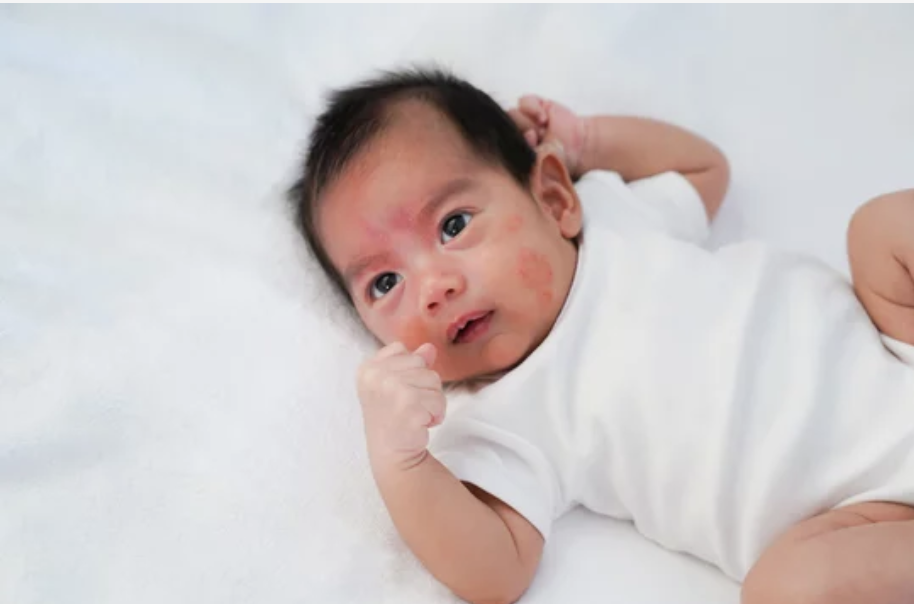
The global prevalence of pediatric atopic dermatitis increased from 1990 to 2019.
Anxiety regarding accidental allergen exposure may create stress for patients and affect their quality of life.
Education on early introduction of allergenic foods is crucial to prevent food allergies.
Psoriasis was linked to greater odds of asthma and eczema.
Panelists discuss how physicians and allergists can distinguish between food intolerance and anaphylaxis.
Dr. Powell highlights how socioeconomic status and race influence the prevalence and management of food allergies.
Children residing or attending school in historically redlined neighborhoods had more severe asthma.

















 © 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.
© 2025 Mashup Media, LLC, a Formedics Property. All Rights Reserved.